Treatments, Galga of Cancer
Cancer data is bittersweet. Salinity, because it is cancer, is the disease that causes more deaths after cardiovascular diseases, both in Euskal Herria and in Europe in general. In addition, some cancers have increased their incidence in the last decade. But they are also sweet: in the same period of time mortality has decreased and the quality of life of patients has improved greatly. This good evolution is largely due to the improvement in treatments.
Arrate Plazaola, doctor of the Onkologikoa of San Sebastian, has been treating patients with cancer for years, so he is a direct witness to the advances in treatments and their influence. "The main treatments remain surgery, radiation therapy, and drugs, but there have been significant improvements in all of them," explains Plazaola.
For example, surgery is a common treatment in some cancers. It is ideal if the cancer is localized and has not spread. Thus, it is very used for the treatment of skin, lung, breast and colon cancers, among others. If the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, they are also removed in some cases. In any case, the goal is to eradicate all tumor cells to avoid the risk of reappearance and expansion of cancer.
In this regard, Plazaola considers that advances in surgery have had a great impact on the quality of life of patients: "With microsurgery, laparoscopies, etc., operations are more accurate and agile than before and have a lower risk of infection."
In fact, to reach the site of the tumor, instead of making open cuts, small incisions are currently made, by which optical and surgical instruments are introduced. In addition, in cases where it is possible, they use natural holes in the body to reach the tumor. Plazaola summarizes the benefits of these techniques. "This allows that after the intervention the patients hardly suffer pain or discomfort, so they can go immediately to their home. In this way, the hospital stays have been greatly summarized".
In addition, the current trend is to keep as many healthy tissues as possible. For example, in kidney cancer, the entire organ was usually removed. The tumor is now removed from the kidney and the part is left healthy. In this way, they prevent the patient from losing a kidney. In fact, they have shown that patients with more kidney mass are those who live longer. Another example is breast cancer, although sometimes it may be necessary to remove all breast to prevent the spread of the disease.
Mutagenic radiation against mutated cells

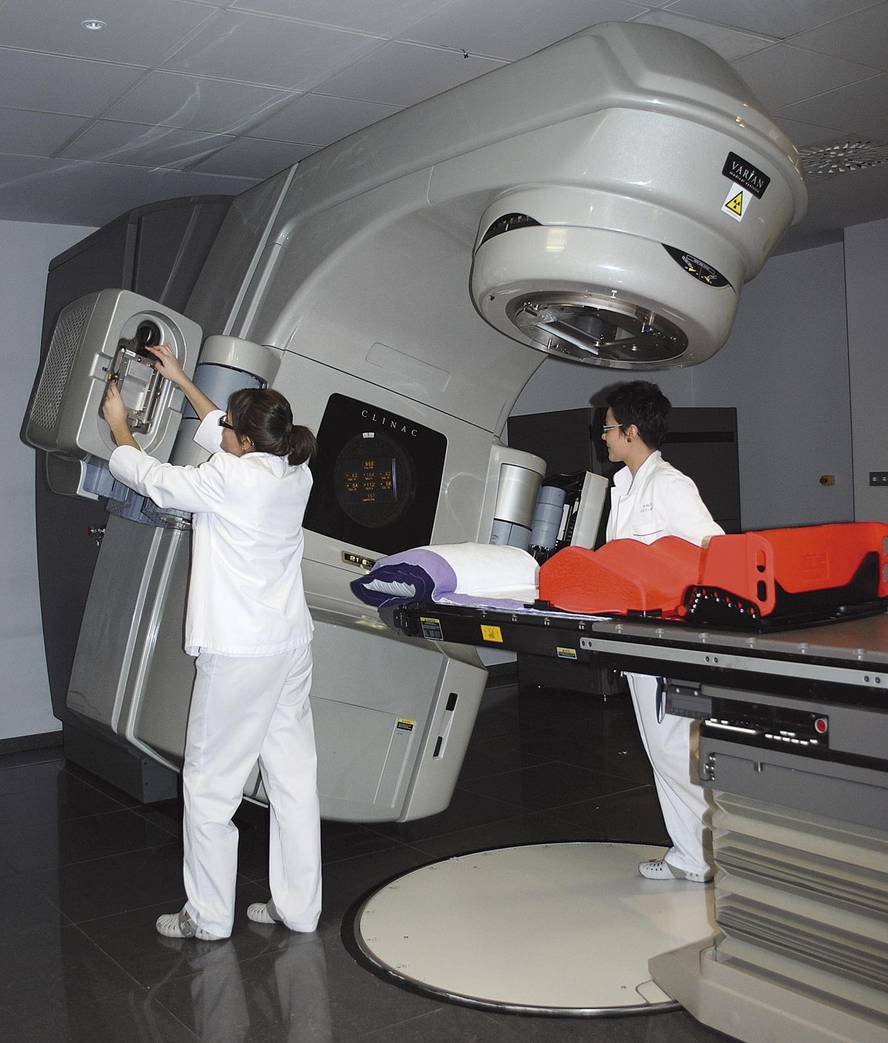
In some cases, surgery is not enough to remove cancer, and doctors need to use other therapies such as radiation therapy. In this type of therapy, ionizing radiation is used to kill cancer cells, which damage the DNA of these cells, causing them to die. However, radiation also affects healthy cells, so doctors take strict measures to limit the area to be treated.
In this regard, Plazaola expresses his gratitude for the progress made: "It is to be grateful that your research advances are applied in a technology that we can use." However, he also pointed out the difficulties: "It is undeniable that current technology makes things easier for us, but to some extent it makes us difficult." According to him, the plans are usually very heavy, "for example, in tomotherapy".
Tomotherapy is the most recent technique they have in the oncology. Plazaola has given some brushstrokes about its benefits and difficulties: "This same radiant apparatus is responsible for the manufacture of scanners, which allows to know daily the delimitation of the area to be treated. But it's complicated and requires a lot of time."
In fact, the scanner allows to obtain highly accurate images in which healthy tissues and tumors are distinguished. The type, size, location, and other abnormal tumor factors determine the radiative treatment to be implanted. Then, the same device emits radiation.
Therefore, to avoid damage to healthy tissues, it is essential that the patient always remain in the same position, both in pre-treatment preparations and every time the treatment is going to be received. "And that's getting heavy, it's not easy," says Plazaola. But it has great benefits: "Yes, then the treatment is much better, more precise, it does not harm normal tissues... In that the improvement is very evident".
In addition, it considers that the sequencing of radiation treatment has greatly improved. "Before, for example, we did 40 sessions and it was very long. At present it is done in less time, perhaps two weeks, and the sessions are held every 12 hours. That is, although the total radiation is the same, the form of administration has changed and the patient supports it better".
This is very important to Plazaola: "It is essential to preserve the quality of life of the patient. After all, we have to heal, heal, maybe we have not cured it so much, but at least we have to try to make them as good as possible in the time they are alive."
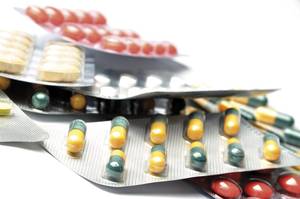
From chemotherapy to biological therapies
Oncologists have another weapon to fight cancer: chemotherapy. It is based on cytostatic and cytotoxic drugs, that is, substances that prevent or destroy cell growth. There is a great variety and each drug has its mechanism of action, degree of effectiveness, specificity... and side effects.
In fact, the drugs affect cells of rapid division, one of the characteristics of tumor cells is their rapid division, but not only of them, but also of healthy cells of the blood, hair or the digestive system. Therefore, these cells are also affected by the drugs given in chemotherapy, which produces side effects such as risk of infection, fatigue, discomfort, nausea, diarrhea, ulcers in the mouth and throat, lack of appetite, hair loss, thinning, etc.
Physicians, of course, try to make the side effects as mild as possible, prescribing in each case the most appropriate medications, doses, and instructions, but researchers have also made a special effort to get drugs that specifically affect tumor cells, hence biological therapies. "It's in this field where more progress has been made," says Plazaola.
As the researchers clarify the mechanisms that affect the life of cancer cells, the doors to pharmacists are opened to design new drugs at key points. Plazaola has compared destinations with the instrumental keys: "Little by little we are discovering the keys of tumor cells and are inventing drugs for each key."
The destinations of these new drugs are very varied: enzymes, genes, proteins... and drugs are designed specifically for each of them. Therefore, they are very specific, they only affect tumor cells and have no effect on healthy cells.
Plazaola puts the example of Herceptin. Herceptin (trastuzumaba) is a monoclonal antibody created in the laboratory. Its destination is the protein controlled by the HER2 gene. This protein is the receptor of a growth factor, expressed disproportionately by some tumor cells, in which case cancer increases rapidly. In addition, the risk of cancer reappearance after treatment is very high.
Between 25 and 30% of breast cancers are her2-positive, that is, in more than a quarter of breast cancers, tumor cells have increased the expression of the receptor associated with the growth factor. "In these cases, Herceptin is of great help," said Plazaola. The antibody is associated with the receptor, so the signal that boosted tumor growth is removed.
Herceptin has side effects (among others, it causes heart problems), but benefits are greater than damage. In this regard, last year the European Union authorized the use of Herceptin also in her2-positive stomach cancer. In addition, researchers are testing many other molecules to touch and silence other keys, some of which are already used in conventional treatments.
Hormonal therapy
However, the classic example of biological therapies is hormonotherapy. The basis is that some hormones promote the growth of cancer cells. Therefore, the use of molecules that act in this mechanism paralyzes the growth of cancer cells.
In the chest, for example, tamoxifen has been used for years. This molecule binds to estrogen receptors, thus releasing place to estrogen. "In 80% of breast cancers, cells have estrogen receptors, that is, they are extremely dependent," explains Plazaola. "Therefore, in many cases we treat the patient with tamoxifen after surgery to prevent the recurrence and spread of cancer."
After tamoxifen, the researchers have also developed other molecules that hinder the action of hormones. Plazaola mentions aromatase inhibitors: "Aromatase is an enzyme that participates in the production of estrogen. These inhibitors prevent the function of aromatase, so no estrogens are generated". This treatment gives very good results in women with menopause.
In prostate cancer there are also molecules that prevent hormonal action. In fact, in many prostate cancers, tumor cells need testosterone to grow. Even when prostate cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body, treatment is also due to the need for testosterone. In this way, molecules that block the production of testosterone or prevent the binding of the hormone to receptors are effective against these cancers.

If the cancer is not dependent on hormones, hormonal therapy is not affected, so doctors recommend chemotherapy. However, in most cases, all types of treatment combined are used. In each case it is a combination or another, and in all of them the goal is double: to eliminate the cancer and get the patient to have the best quality of life possible.
Priority, patient welfare
As for the well-being of the patient, important efforts have been made to alleviate the side effects of treatments. "Now, along with treatment, we give a new therapy to patients to protect them from the damage caused by radiation or the drugs we use against cancer," explains Plazaola.
It is called support therapy and is adapted to the patient. "For example, when we know that our treatment will reduce defenses, from the beginning we give the patient a medicine to recover the immune system. In this way the risk of infections is considerably reduced".
Psychological support is also offered to patients. According to Plazaola, depending on the emotional state and nature of the patient, psychological assistance is offered from the beginning, and sometimes psychological therapy is done after other treatments. However, for many patients it is "very useful".
Asking for your opinion on the quality and effectiveness of treatments, Plazaola has no doubt: "Taking into account the international situation, in Euskal Herria there are the most cutting-edge treatments". In this sense, a point of pride is noted, but at the same time fears that the current economic context does not affect the offer of public medical services because "these treatments are very expensive: the appliances are expensive, even the medicines, the service..."
However, look to the future with optimism. Among others, he believes that studies on circulating tumor cells will give useful results. "We know that circulating cells spread cancer, through them metastases appear, but we still do not know many other things." This is one of the lines that are being investigated the most and Plazaola expects important improvements to be made: "They may get an anti-regulatory substance and, in that case, we can completely eliminate the cancer."





