A new technique to turn other brain cells into neurons
Other brain cells have managed to turn them into functional neurons in mice and isolated human cells through a new one-step technique. This technique has managed to restore the symptoms of the disease in Parkinson's mouse models, and researchers believe it could be a new way to treat neurodegenerative diseases. The study has been published in the journal Nature.
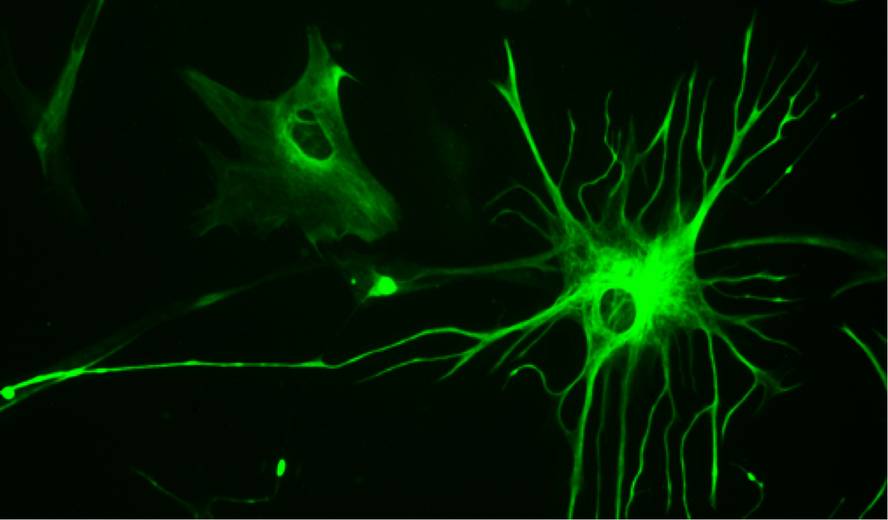
One of the main objectives of regenerative medicine is to replace neurons that are lost in neurodegenerative disorders and get new neurons to integrate into neural circuits. For example, dopaminergic neurons are lost in some areas of the brain. Well, in this new research they have shown that some abundant cells in the brain, astrocytes, can become dopaminergic neurons.
Astrocytes produce a protein called PTB that makes the astrocyte not become neuron. Thus, in the mouse models of parkinson, by excluding astrocytes from the disease-affected area the PTB protein, it has been observed that neurons become fully functional, repopulating the reduced neuronal circuits and therefore regenerating the level of dopamine and motor functions. In addition, they have found an effective method of temporary elimination of the PTB protein: the use of oligonucleotides that block messenger RNA containing information for protein production.
However, researchers have warned of the need to investigate further to use this technique in humans. For example, about 65% of the astrocytes to which the technique has been applied have not become neurons, something that should be improved. On the other hand, it should be analyzed whether the elimination of PTB proteins or the techniques used for this present lateral damage.