Cannabinoids cause energy loss of neurons
Brain cell activity requires great energy support. Neuronal mitochondria must produce energy continuously. But cannabinoids directly inhibit this process and the consequence is evident in the brain: amnesia.

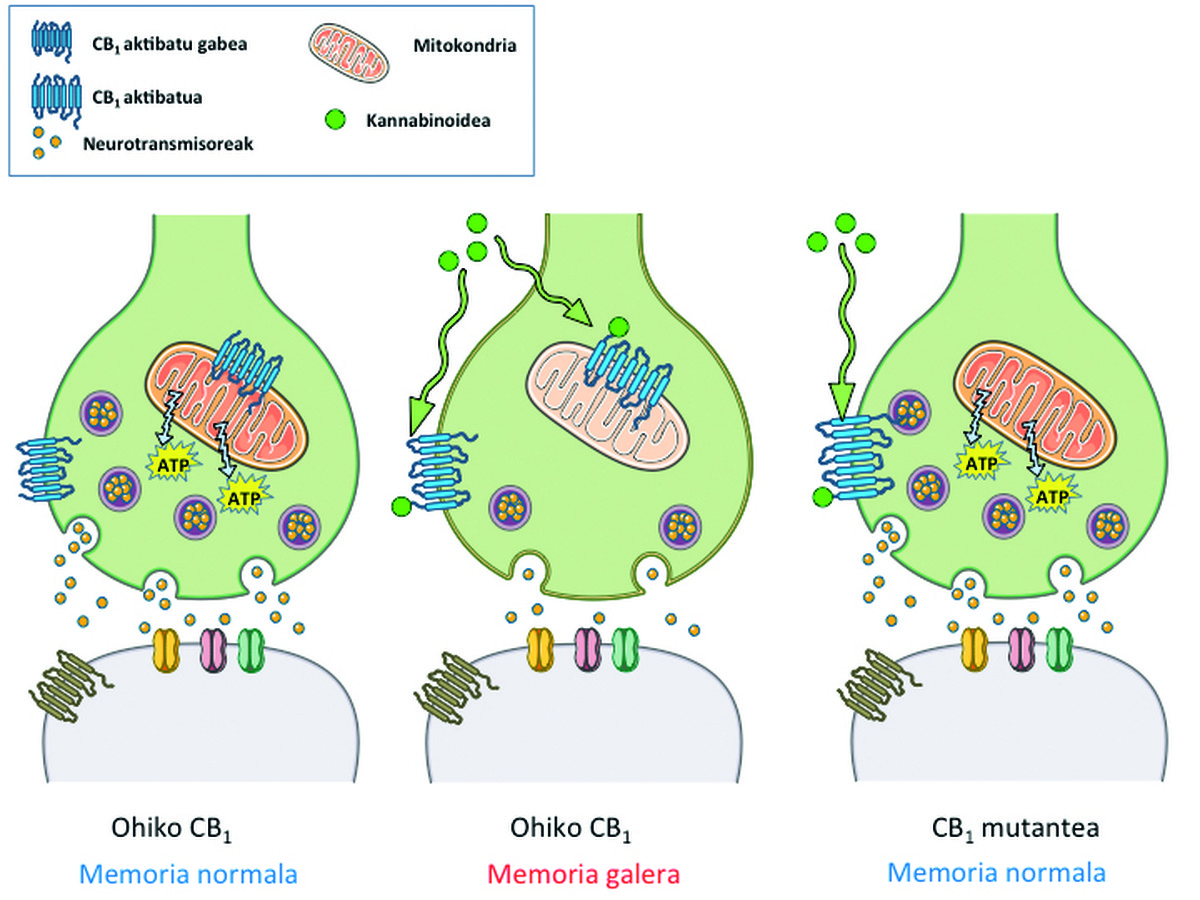
Both the cannabinoids produced by our body and the cannabinoids of the Cannabis plant cause a loss in our memory, which hinders communication between neurons. Inhibition of some neuronal membrane receptors causes neurotransmitters to only be generated. So far it was thought that cannabinoids influenced the plasma membrane of neurons, but now they have seen that they also influence mitochondria membranes. They thus manage to block the power generation in the mitochondria.
The journal Nature has published the new study by researchers from the Department of Neurosciences of the UPV in collaboration with French researchers. “The malfunction of mitochondria can have serious consequences on the brain. For example, chronic mitochondrial dysfunction influences the appearance of neurodegenerative diseases, such as stroke or diseases related to aging,” said the head of the research group Pedro Grandes. “But until now it was unknown that the reduction of the respiratory cell also affected the superior functions of the brain, such as memory.” New research has shown that cannabinoid mitochondria receptors regulate processes such as learning and memory through energy metabolism.
CB1 is the receptor known to cannabinoids. It appears in presynaptic terminals of neurons, but also in mitochondrial membrane. Researchers' work has shown that the elimination of CB1 receptors from mitochondria does not reveal the influence of cannabinoids on memory. Therefore, the reduction of energy caused by the CB1 receptor of the mitochondria and its inhibition is directly involved in memory loss. The key to this has been the CB1 mutant receptor created by researchers: in the plasma membrane itself, but it does not appear in the mitochondria.
Cannabinoid derivatives offer many therapeutic possibilities, but their use is limited due to their side effects, including memory loss. In the opinion of research researcher Izaskun Elezgarai, the discovery opens up opportunities for the future. “This mutant can be used as a tool for drug research and design. For example, a treatment strategy for neurodegenerative diseases or stroke may be the creation of a medicine that influences mitochondria. A medicine aimed at mitochondria that does not go to the plasma membrane may be designed. Or it can cause closure of the mitochondria receptor.” Research has opened up new avenues for more effective and safe medicines for the treatment of brain diseases in the future.





