The most effective non-pharmacological measures that prevent the dissemination of COVID-19 have been identified
Extensive international research has evaluated the main non-pharmacological measures taken in 79 territories to alleviate the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Since the appearance of the first cases of COVID-19, and taking into account those used in the different moments of the pandemic, the aim of the research is to clarify which have been the most effective of all of them. Four independent methods have been used to analyze all international data that combine statistical tools and artificial intelligence. The integration of these four independent methodological perspectives endorses the conclusions.
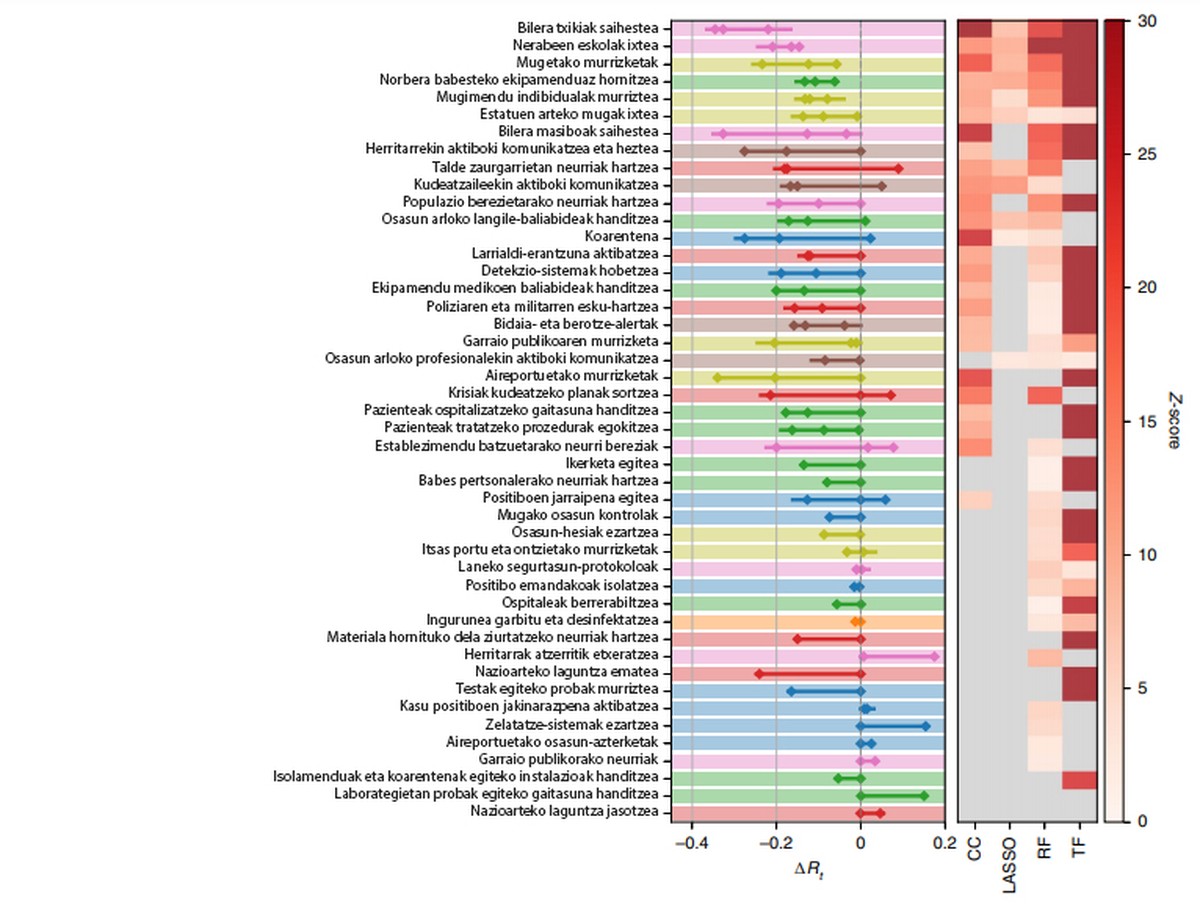
Research shows that there are no miraculous measures to prevent the spread of covid-19, but there are measures that properly combined significantly reduce the value of Rt (average number of people infected by a contagious person) below 1. It has been proven that the most effective are the reduction of travel, closures and closing of meeting places. Mainly closing shops, bars and restaurants, avoiding meetings of 50 or less people, working from home and closing schools of teenagers.
However, the researchers point out that extreme measures have negative consequences: the closure of the institutes has interrupted the learning process of adolescents and has caused social isolation, stress and inadequate nutrition of young people; domestic confinement has led to an increase in cases of domestic violence and an impact on many women and children; it has interrupted the treatment of other diseases and has left serious consequences for the health of many people. As a result, and in spite of the fact that, in general, these extreme measures are the most effective, in view of the serious indirect damage affecting society, the economy, mental health and human rights, governments have proposed to adopt less stringent measures to avoid to the maximum the spread of the virus, but allowing a more acceptable balance between benefits and disadvantages.
Among these milder but effective measures, the most effective is that governments develop a good communication strategy, according to the results. That is, a communication that aims to give clear information about covid-19 and train people. Among the most effective messages are: encouraging people to stay at home, promoting social alienation in the workplace, and security measures, and promoting the isolation of people with symptoms, always on their own initiative. In fact, they stressed that the measures imposed by force have not been at all more effective. They point out that the most effective measures are communication of the importance of social alienation and social empowerment, since the population meets them better. In addition, they are measures that can be easily adopted by countries with economic difficulties to increase their resources in the health system.

Aid programmes created by governments for vulnerable populations, especially food programmes and financial aid, have also been effective. According to researchers, Rt reduction can help establish measures that help isolate people who are going to be isolated without fear of losing work or salary.
At the other end, among the ineffective measures are disinfection and cleaning of surfaces and objects in public and large places. Nor has the closure of parks, public museums, etc. In addition, they have found no evidence of the efficacy of measures of social alienation in public transport in cases in which it has been used for free. In fact, the effectiveness of the biblical has been very effective in three of the four methods.
On the other hand, it is commented that the tracking and tracking of the positives has not been as effective as expected, especially because in many cases the tracking and tracking capacity has been low at the beginning of the pandemic and has been implanted with delay.
The researchers have clearly indicated that most governments have taken very restrictive measures against the covid-19 pandemic, sometimes intrusive. They had to make decisions in changing epidemiological situations and there was no scientific evidence on the effectiveness of the measures. However, in future plans it has been proposed to take into account the results of the research, always valuing the local characteristics and the concrete state of the pandemic, since they can be decisive for the management of the following waves of covid-19, as well as to face in the future other possible viral epidemics of the respiratory system.
The efficacy results of all the non-pharmacological measures analyzed are as follows. At the top of the list are shown the most effective measures according to the four methods. Less effective measures at the bottom of the list.