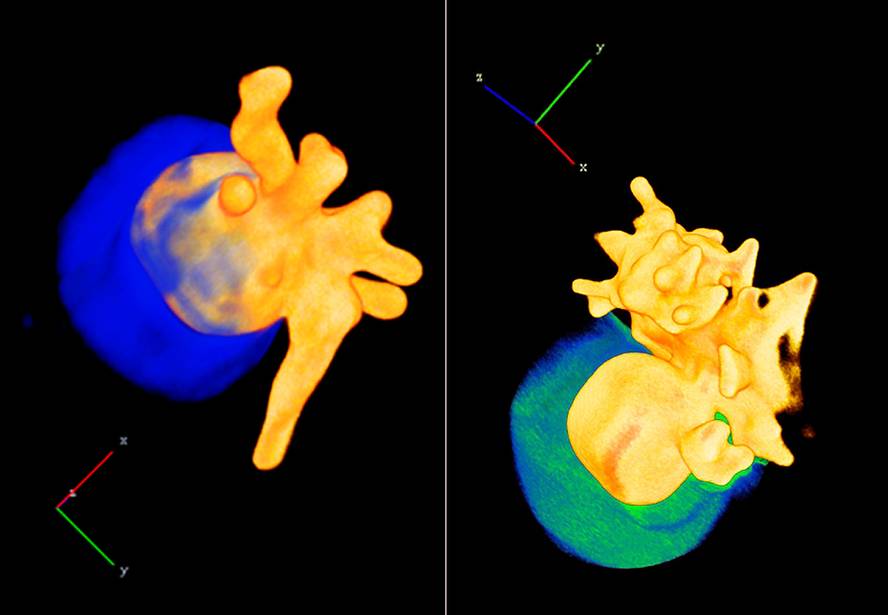
CIC bisisGUNE designs nanoparticles with a silicon face and a gold face
Researchers at CIC bioma GUNE and the University of Antwerp (Belgium) have designed half-gold nanoparticles and the other half silicon oxide. They are a type of Jano particles, so called in honor of the two-sided Roman god. This is the particularity of Jano particles: the conjunction of very different physical properties in one body. The CIC biome GUNE researcher has silicon oxide on one side and gold point on the other in the form of star and nanometer size.The CIC biome researcher GUNE, Luis Liz-Marzán, has told the SINC agency that "the optical and electronic properties of these nanostars depend, mainly, on the small dimension of particles and their morphology." In this case, the researchers have developed techniques of molding sharp gold tips, which allows them to create high intensity electric fields through the light in the gold needles.
The manufacture of nanoparticles is done in different stages. First, the gold nanospheres are created, through the chemical reduction of a metal salt. Next, a different organic compound is added to each side of the particle so that they have different affinity with silicon oxide. In this way, the oxide covers only one part and the other is exposed so that the gold tips grow in it.
“Ours is a basic research,” says Liz-Marzán, “but these areas are used in ultrasound detection processes to identify small amounts of adsorbed molecules in the golden part, such as contaminating agents or biological markers that alert to a disease.” Another possible application is phototherapy, the death of malignant cells by heat, by applying light to gold tips. They would use the oxide face to associate the nanostar to the biological receptors specific to the affected cells, where gold fragments would fulfill their therapeutic or diagnostic function.The results of the research have been published in the journal Chemical Communications.