The influence of cannabinoids on glucose metabolism reduces social interaction
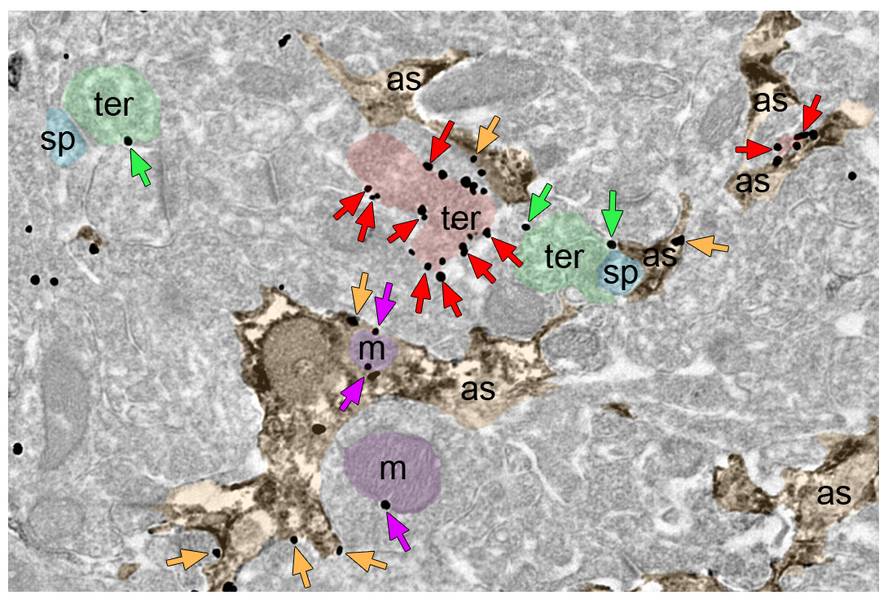
Astrocytes capture glucose from the bloodstream to give energy to the brain. At the same time, astrocytes are controlled by neurons through neurotransmitters. Other elements that influence this control are, for example, the receptor of astrocytes (receptors of canavidoids type 1 or CB1), which are the main target of the psychoactive component (THC) of the hemamo.Researchers of the Department of Neurosciences of the Faculty of Medicine and Nursing of the UPV/EHU and of the Achucarro Center have tried to clarify the collaboration of the
Studies with mice have found that the activation of cannabinoid receptors CB1 in astrocyte mitochondria prevents the metabolization of glucose and the formation of lactate in the brain. In this way, there are alterations in the neuronal function that affect the behavior of social interaction.
The study has been published in the journal Nature. It is explained that when these receptors are activated, astrocytes produce fewer reactive oxygen species, which affects the glycolytic production of lactate. This causes neuronal stress and decreases social interaction.