New Horizons probe results published
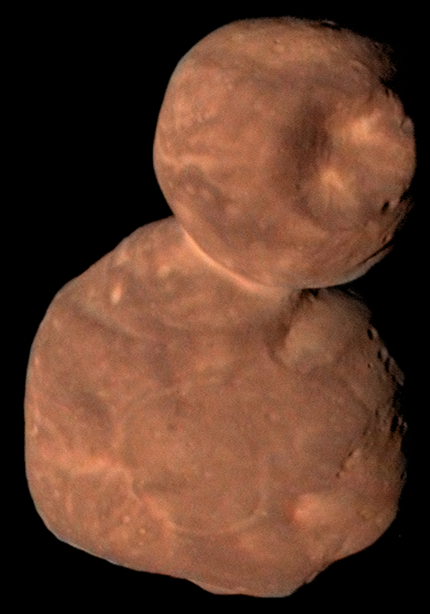
Since the New Horizons probe reached Ultima Thul, the first results have been published in the journal Science. Ultima Thule (2014 MU69) is the furthest body in the universe studied closely by a probe: Beyond Neptune, in Kuiper's belt, among other thousands of asteroids and millions of comets, they have declared that it is the most red object ever seen in the solar system. Evidence of methanol, icy water and organic molecules were found on the surface, and they believe that reddish color can be the result of the transformation of this organic matter.
Other characteristics such as bright surface spots, valleys and hills, craters and holes are being studied, among others. The largest depression they have discovered has a width of 8 km and is believed to occur with an impact. However, NASA researchers claim that smaller holes can be caused by ice.
It is a two-lobed object. The largest is called Ultima and the smallest is called Thule. At first they believe that they would orbit apart but as a binary object and subsequently merged. In view of the alignment axes, it is suggested that they would have the same areas that merged, while they were orbiting around the same point.
At this time, in view of the distance of Ultima Thul to the Sun, and being a stable orbital, researchers believe that it would not suffer just variations since the formation of the solar system, due to the low radiation that would affect. Thus, they have foreseen that it is an object of great value to investigate the beginnings of our planetary system as a space fossil.
400




