Clarify the mechanism of pigment that protects us from solar radiation
Melanin is known to color hair, skin and eyes, protecting the body from ultraviolet solar radiation. Specifically, a form of melanin has eumelanin protective capacity. But until now they didn't know what that capacity gave them. This is what MIT Massachusetts researchers have explained, in collaboration with others.
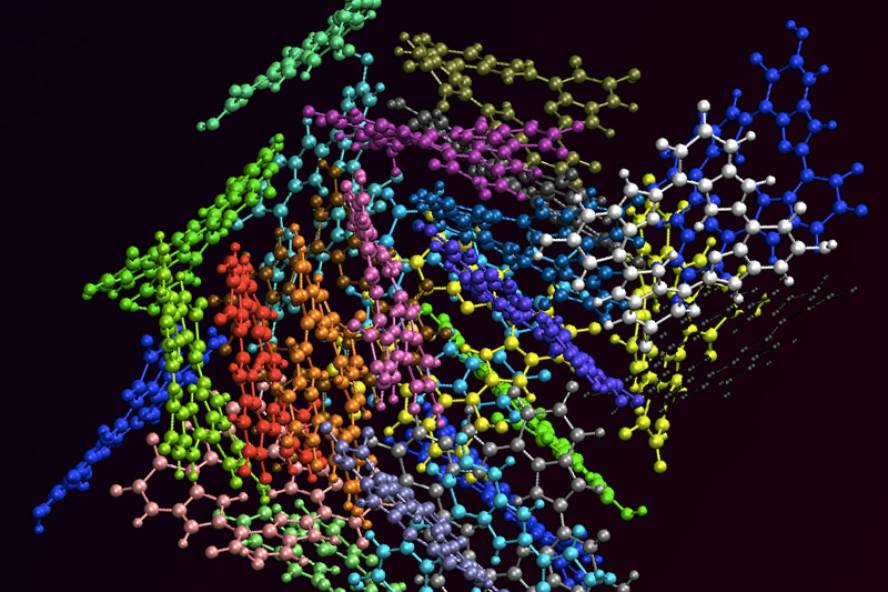
The research has been made known in the specialized journal Nature Communications and have explained that the key is in the molecular structure. In the case of eumelanin, this technique has not been enough to expose its secrets. Therefore, researchers have combined computer tools with experimental analysis, which has allowed us to verify that eumelanin owes its function, not only to the components.
It seems that eumelanin has a part of its geometrically arranged components and a mixed form that blocks ultraviolet. According to the researchers, eumelanin “is a natural nanocomposite”. In addition, they have seen that, although the basic structure is the same, there are more than one hundred variants, which explains the difference between each other in the blocking of radiation.
Researchers have stated that knowledge of the characteristics of eumelanin may be useful for the generation of new synthetic materials, and one of the applications may be to increase the efficiency of solar cells.